In the 70s aluminium was used in construction, however it lacked strength - it was not resistant to pressure. The nonferrous metal was consequently substituted by carbon alloy - carbon fibre.
A fibre is always substantialy stronger than the same material in its compact form. The reasons are: - small cross section of the fibre - the preferential direction of the permanent homopolar atom bonds in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the fibreFibres of homopolar atom bonds get the biggest elastic modulus, where the planes of the crystal lattice parallel with the fibre axis are mostly occupied. Such fibres are remarkably anisotropic, i.e. their features in the direction of the axis and normal to it are substantially different.
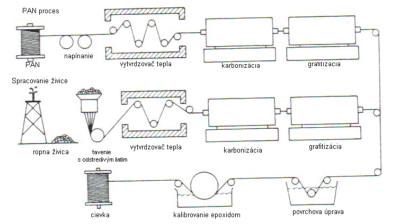 |
Fig. 01
|
CARBON FIBRES
They are made from polyacrylnitrite fibres (PAN) or from interfacial resins, processed remains of oil distilation. The PAN being the most frequent in production.The theoretical strength of the graphite monocrystal subjected to tension in the direction parallel to the base planes is about 100 GPa and the theoretical elasticity of elongation is about 1000 GPa.The massive strength and rigidity of the aromatic planes is used in carbon fibres, where the planes follow the direction parallel to the longitudinal axis of the fibre.The strength of fibres (up to 7000 Mpa today) is ensured by tiny microcrystals and minimal number of defects among them. The size of the carbon fibres' microcrystals of PAN may be divided into 3 stages. 1. at temperatures of 220 to 300ÂşC, under tensile stress in oxidizing atmosphere the PAN fibre gets stabilized. The fibre turns black and becomes infusible. 2. at temperatures of 1000 to 1500ÂşC the fibre carbonizes (hydrogen is removed and the concentration of nitrogen and oxigen is cut down, carbon represents 80-95% of the mass) 3. at temperatures of 1800 to 3000ÂşC graphitization is obtained. The contents of carbon is increased allowing more perfect microcrystals to emerge.
 |
Fig. 02 - Graphite structure for PAN - the base for a carbon fibre of 400 GPa
|
Features:
- elasticity modulus is substantialy lower, at the level of polycrystalic graphite
- fragility - higher fragility appears during bending
- the fibre gets shorter when heated up
- good or excellent heat conductivity
- good electric conductivity
 |
Fig. 03
|
 |
Fig. 04
|
 |
Fig. 05
|
|