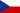
Shock absorbers
Miroslav Sanytrák/Boris Dacko/foto J.Křenek | 10.2.08 | Tlumiče
F1 construct
The shock absorber absorbs bumps from irregularities on the road and prevents their transfer further onto the chasis, which would put a stress load on it, and furthermore it keeps the oscillations of unsprung mass to minimum, so that the wheels would stay in contact with the road. This has a positive effect not only on the transfer of the braking and driving forces, but also on the lateral forces when the car is cornering. Hence, the absorber absorbs not only shocks but also oscillations. From the physics point of view, the shock absorber takes mechanical energy, changing it into the heat energy, similarly to brakes. The difference is, however, that brakes dump the energy through friction, while the shock absorbers through the hydraulic resistance. A shock absorber is, of course, closely linked to the spring element, which is usually a wound spring or a torsion bar. The front suspension most often features a coaxial installation of the spring and the shock absorber, while those two elements are, for the reasons of space and aerodynamics, located inside the car, the axles' movements being transferred onto them via a diagonal pushrod. As far as the rear axle is involved, most often you can see the torsion bars and independently installed shock absorbers. Obviously, there is a number of other combinations possible, the one above is, however, most frequent. The springing is also accompanied by antiroll bars. As far as the shock absorbers alone are involved, there is a number of systems, but each team keeps their specific type and characteristics a secret.
 |
The F1 shock absorbers can be hydraulic, where the heat is dumped in oil. There are high demands on the technology of the inner vents, causing the necessary resistance, but also on the oil. Oils and liquids are very sensitive to the heat and change their viscosity depending on it. Therefore there is a lot of attention paid to the research of oils that would react to the temperature change as little as possible. There are also gas shock absorbers using nitrogen as medium. Though those need an extra container for the gas. The teams also need to set the intensity of the dumping effect both, for the shock and rebound. Therefore the performance shock absorbers offer really a wide range of possible adjustments. They always work with two pre-set characteristics, where the slower one is used for dumping forces and oscillations through the acceleration, braking or cornering, while the faster characteristics is used for fast oscillations which are the result of irregularities of the road. Such a double-characteristics is possible due to a pair of vents in the shock absorber. That is why the mechanics have to set the characteristics of both "slow and fast" vents prior to each race.
 |